Edge computing is no longer just a buzzword- it’s the backbone of the digital age. By moving processing power closer to the data source, it enables faster responses, better security, and more efficient use of resources.
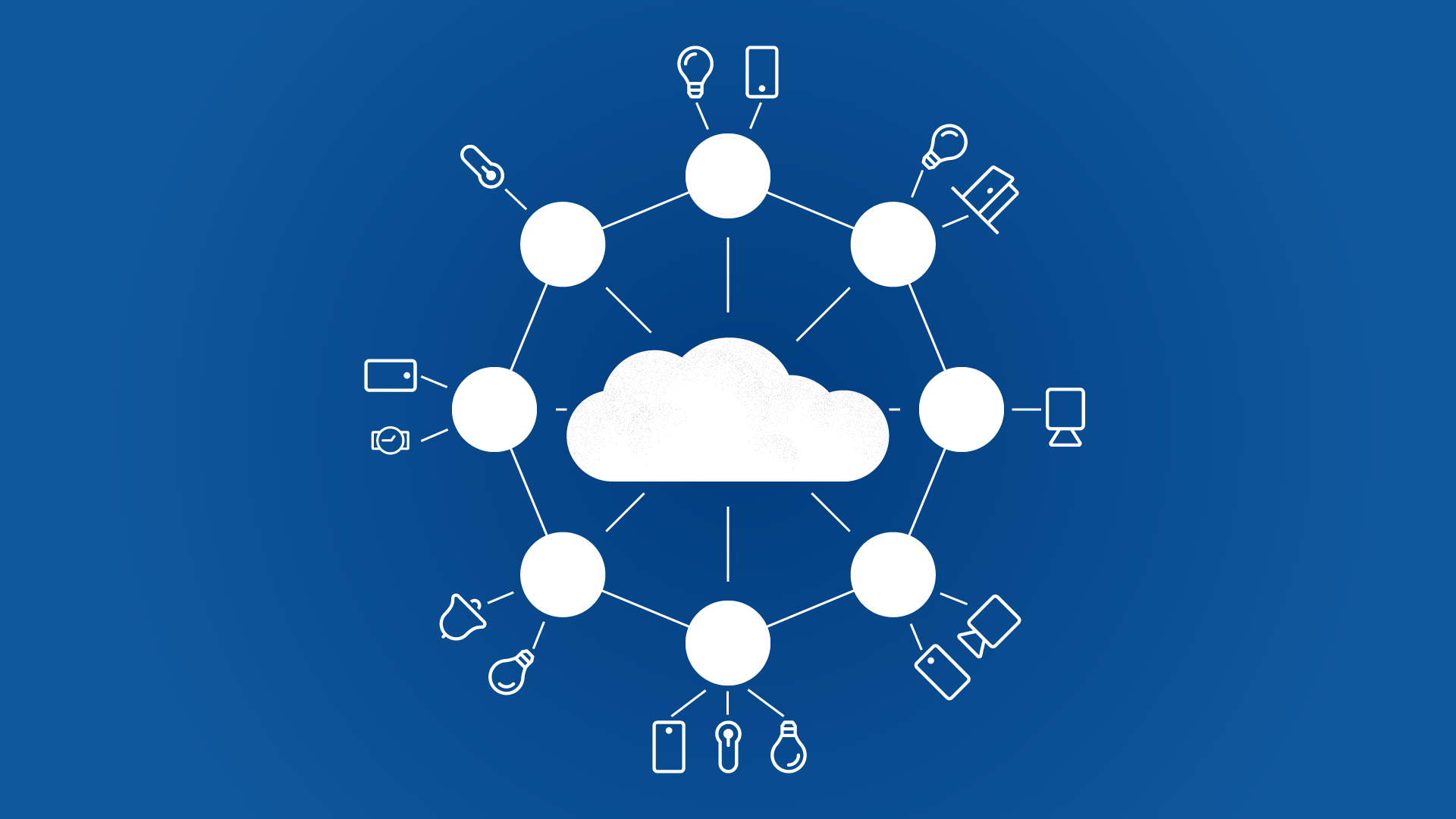
The digital world is generating more data than ever before. From smartphones and smartwatches to autonomous cars and industrial sensors, billions of devices are constantly creating and transmitting information. Traditionally, all this data is sent to centralized cloud servers for storage and processing. But as the volume of data grows and the need for real-time responses increases, this model is no longer efficient. Enter edge computing-a revolutionary approach that brings computing power closer to where the data is generated.
In 2025, edge computing is more than just a trend; it’s a necessity for businesses, industries, and even everyday consumers. But what exactly is edge computing, and why does it matter so much today?
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is the practice of processing data near the “edge” of the network-closer to the devices and sensors that generate it-instead of relying solely on distant cloud servers.
For example, consider a self-driving car. It cannot afford to send data to a cloud server thousands of miles away and wait for instructions. It needs real-time processing to make decisions like stopping at a red light or avoiding a pedestrian. Edge computing makes this possible by handling the processing locally, right within the car or nearby servers.
Why Edge Computing is Growing
1. Explosion of IoT Devices
By 2025, there are an estimated 30+ billion connected devices worldwide. From smart homes and wearable health trackers to factory machinery, these devices generate massive amounts of data every second. Sending all that data to the cloud is costly and slow. Edge computing reduces this burden by processing much of it locally.
2. Demand for Real-Time Processing
Applications like autonomous vehicles, augmented reality (AR), telemedicine, and online gaming require ultra-low latency. Even a delay of a few milliseconds can result in accidents or poor user experience. Edge computing ensures data is processed instantly, making real-time responses possible.
3. Reduced Bandwidth Costs
Constantly transmitting raw data to the cloud consumes bandwidth and increases costs. With edge computing, only the most important or refined data is sent to the cloud, while the rest is processed locally. This helps organizations save money while keeping networks efficient.
4. Enhanced Privacy and Security
Data privacy is a growing concern. Edge computing helps protect sensitive information by keeping it closer to the source. For example, a smart health monitor can analyze patient vitals locally and only send necessary insights to the cloud, reducing the risk of sensitive data being intercepted.
Key Applications of Edge Computing in 2025
- Healthcare
Hospitals and wearable devices use edge computing to monitor patients in real time. For example, a wearable ECG monitor can detect irregular heartbeats and alert doctors instantly-without relying on distant cloud servers. - Smart Cities
Traffic management systems, security cameras, and energy grids all rely on fast data analysis. Edge computing helps reduce congestion, improve public safety, and manage energy consumption more efficiently. - Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars depend heavily on edge computing to make split-second decisions. With sensors constantly scanning the environment, edge systems ensure safety without delays caused by cloud dependency. - Manufacturing and Industry (IIoT)
Factories use edge computing for predictive maintenance. Machines equipped with sensors can analyze performance locally and alert engineers before a breakdown occurs, reducing downtime and costs. - Retail and AR/VR Experiences
From cashier-less checkout systems to personalized shopping recommendations, edge computing enhances customer experience. Similarly, AR/VR systems rely on edge power to deliver smooth, real-time immersive experiences. - Telecommunications (5G Networks)
5G and edge computing go hand in hand. Telecom companies are building edge data centers to support faster connections, enabling seamless video streaming, online gaming, and IoT applications.
Challenges of Edge Computing
While edge computing is powerful, it also faces challenges:
- Scalability: Deploying and managing thousands of edge devices is complex.
- Security Risks: Each edge node can become a potential attack point if not secured properly.
- Integration with Cloud: Businesses must strike the right balance between edge and cloud computing.
- High Initial Costs: Setting up edge infrastructure requires significant investment.
The Future of Edge Computing
Looking ahead, edge computing will continue to evolve alongside AI, 5G, and IoT. We can expect:
- AI at the Edge: Devices that don’t just process but also learn and adapt on their own.
- Micro Data Centers: Smaller, distributed data centers placed closer to users.
- Stronger Security Models: Built-in encryption and authentication at every edge device.
- More Consumer Applications: Beyond industries, everyday consumers will benefit from faster, smarter apps and devices.
Conclusion
Whether it’s saving lives in healthcare, powering autonomous vehicles, or improving gaming experiences, edge computing is reshaping how we interact with technology. In a world where milliseconds matter, edge computing is the key to unlocking a smarter, faster, and more connected future.
In short, the rise of edge computing is not just about technology-it’s about enabling progress in every area of modern life. Also Check Best App Development Frameworks – Free Guide – 2025


1 thought on “Rise of Edge Computing – Why It Matters – 2025”